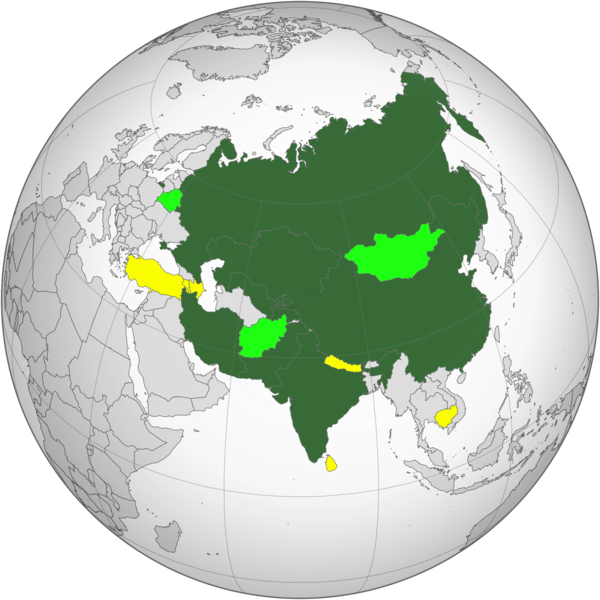
In 1996, Shanghai Five was formed, consisting of Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. Uzbekistan joined the organization in 2001, following which the Shanghai Five was renamed as Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO). In 2017, India and Pakistan became its members.
2021 Key Takeaways
- discussions were based on the ground situation in Afghanistan and its international repercussions.
- Iran was made a full member of the organization.
Today SCO comprises nine members, namely Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Russia, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan, and Iran.
The organization aims to maintain stability in the region along with peace and security. For this reason, it is seen as a counterweight to NATO ( North Atlantic Treaty Organisation ). [ For the article on NATO – click here ]
Its other objectives are to promote cooperation in politics, trade, research, tourism, and other relevant areas. The focus is to develop mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states.
FACTS
SCO’s headquarters is located in Beijing, China.
Its official languages are Russian and Chinese.
Its chairmanship is rotated for a year by member states.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation comprises two permanent bodies – First is its Secretariat based in Beijing. The other is the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) in Tashkent (Uzbekistan). The committee aims to promote cooperation among member states against terrorism due to which all contribute to intelligence gathering in RATS.
SCO can be a potential platform to build a new channel that can enhance bilateral ties between countries. Through intelligence sharing, governments can improve their counterterrorism abilities. The SCO can play a crucial role in stabilizing Afghanistan, especially when there are serious concerns over the humanitarian crisis unfolding there.