Sunni and Shia Differences and conflict is rooted in the question – Who should succeed Prophet Mohammed in leading Muslims after his death in 632 AD?
Shias say that prophet’s cousin and son-in-law, Ali was his rightful successor but he was cheated when the authority went to those who sunnis call the four “Rightfully Guided Caliphs”. Sunnis accuse the Shias of elevating Ali to the level of Muhammed himself.
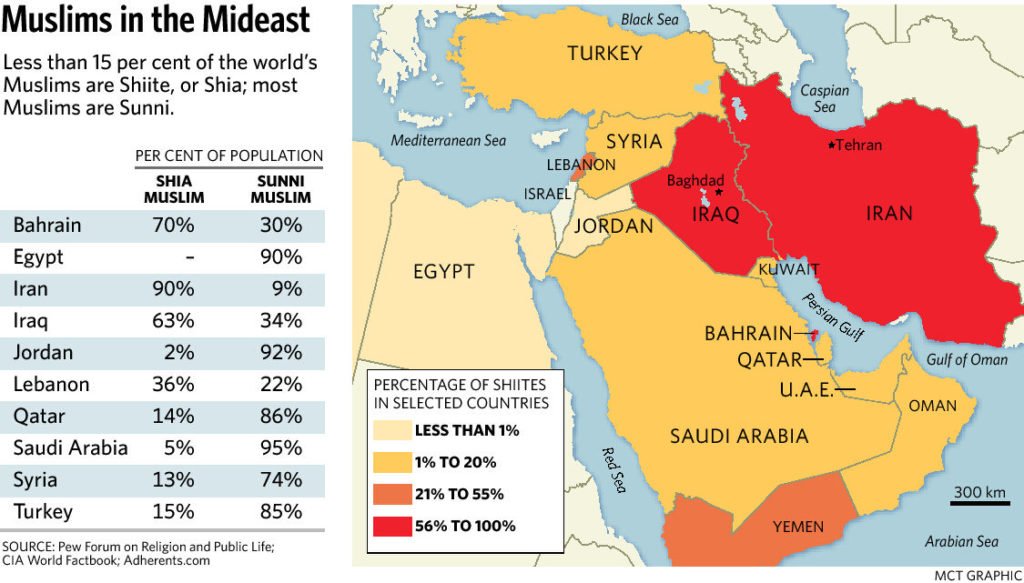
Sunnis are majority across the Islamic world. In the Middle East, Shias have strong majorities in Iran, Iraq and Bahrain.
In Iraq, US led invasion that toppled Saddam Hussein’s Sunni dominated regime in 2003 propelled long-oppressed majority Shias to power. Sunnis felt that the repression would flip onto them. The result was vicious sectarian fighting that lasted until 2008.
In Syria, the fighting was ravaging for more than 3 years between forces that wanted President Assad to stay in power and those who wanted to remove him. This was the situation until 2013. But in 2014, the real threat was the rise of a terror outfit – the Islamic State (IS). This terror outfit was more radical than Al-Qaeda and more aggressive than LTTE in its military planning.
Crisis in Syria:
Crisis in Syria had become one of the biggest humanitarian crisis since world war II. In 2013, the main villain was Assad government in Syria. In Syria, a Shia leader was holding power in a Sunni dominated state for years. The key supporters for the Syrian government were Iran and Russia. On the other hand, rebels were supported by Saudi Arabia, the US and Turkey.
The reported use of Sarin gas (chemical weapon agent) during the Syrian civil war led to an explosive scenario. One side believed (many governments, Arab League and European Union) that attack was carried out by President Assad and the Syrian and Russian government blamed the opposition.
Destruction of Syria’s’ chemical began on Oct 2013 and on June 2014, the last declared chemical weapon was shipped out of Syria for destruction. However, a fresh row erupted in September 2014 when Syria declared 4 new chemical weapon facilities it had not previously disclosed. It also raised worries that IS could get hold of these.
This has been a constant problem with US strategy in the Middle East. Be it Saddam’s non existing nuclear stockpile, Iran’s bulging nuclear or Assad’s chemicals, US has often remained in dark and have suffered.
Leaving the Syrians without a leader is like creating another Libya or Iraq. Among themselves, Sunnis neither have leadership nor unity. ISIS is trying to capitalise on this. But re-election of President Assad in 2014 depicted that moderate Sunnis prefer leaders like Assad more than ISIS.
If Assad been compelled to conduct a multi-candidate election in Syria, he can also be compelled to have a multi-party system in Syria in future and that can make a lot more difference.
Crisis in Iraq:
In Iraq 65% of Muslims are Shias and 35% Sunnis; Kurds are mostly Sunnis too. When Saddam was ruling Iraq, he managed to run Sunni dominated government. But since his demise Shias (who were in majority in Iraq) have controlled power. But for a democratic framework to succeed secularism is must.
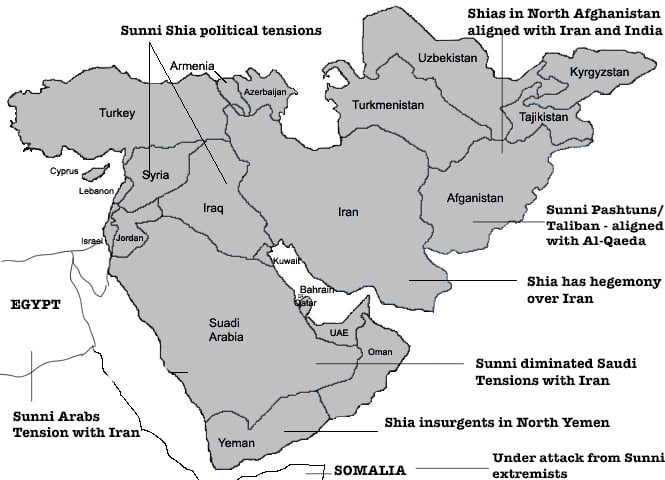
Sunni population has always complained of facing discrimination. Kurds have their own problems. Kurdish peshmerga remains a strong force and can counter ISIS in the north but they are not supported by Iraq because it is believed that given free hand they will embolden their demand for a free Kurdistan. Turkey also fears Kurdish empowerment and as a Nato ally will never allow an aggressive arms supply to Kurds. Southern Iraq is 80% Shia and no force not even IS can control them.
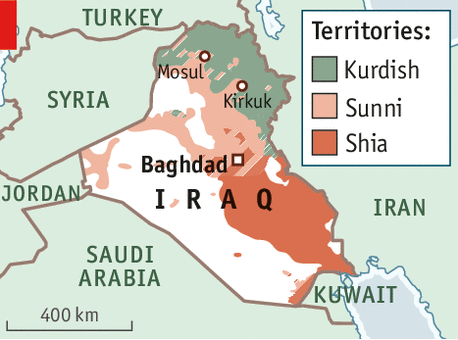
Many mislabel the ISIS invasion as Sunni uprising but this kind of movement led by ISIS which seeks to instil Taliban style dictatorship will be rejected by Sunnis and Shias. With careful handling of the situation, if Shias and Sunnis can unite in a common political vision, it can be translated into a social vision.
What is ISIS and how it spread so rapidly?
Self-declared Islamic state is mainly a muted version of Al-Qaeda in Iraq which operated there since the early 2000s. It has been banned by the UN and US since 2004. However, as the Syrian situation declined rapidly, IS found an opportunity to recruit people and restart its campaign. In 2013, group changed its name to Islamic State of Iraq and Syria and started to grow faster under the leadership of Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi (because the area being rich in oil resources it was becoming worlds’ richest terror outfit)
As the Syrian situation was chaotic and the outfit was being supported by distressed Sunni elites of Iraq (after the death of Saddam Hussain) and former members of Saddam Hussein’s’ Bath Party, it quickly consolidated its position in Syria and then turned towards Iraq where Maliki government was rapidly losing the trust of Sunni population.
On 29th June 2014, it proclaimed that territories under its control would be the core of a new Caliphate regime. It claimed religious authority over all Muslims worldwide and aimed to bring most Muslim inhabited regions under its political control, beginning with the region of the Levant which approximately covers – Syria, Jordon, Israel/Palestine, Lebanon, Cyprus and parts of Southern Turkey. Several terrorist organisations (previously linked with Al-Qaeda) are now openly siding with IS.
There was no united front fight against the IS. US did not want to go along with Assad forces in Syria. Similarly, Iraq did not like to work with Iran and Saudi Arabia and Turkey did not work with any of the Shia fragments. All this, Sunni – Shia – Kurds fight, lead to the advancement of the IS.
IS is a sectarian regime, Sunni dominated in its mentality and by vowing to destroy the holy Shia places it has earned the wrath of not only Shias but is also unable to gain any support from Muslim Brotherhood that thrives on fraternity.
Persecution of Yazidis :
Their persecution was the turning point in the conflict because only then US started taking military actions against IS. US, UK and France made emergency airdrops to the besieged Yazidis and provided weapons to Kurdish Peshmerga defending them.
Yazidis are monotheists who believed in benevolent peacock angel. IS view angel as Satan. Under Islamic law as observed by ISIS, Yazidis are officially given the choice to convert to Sunni or die. In August 2014, IS forced them to flee into mountains. It is only after US airstrikes and Peshmerga intervention that they were able to find safe passage and now live in refugee camps.
Efforts to Counter ISIS:
The majority opinion in US was that a large part of support to ISIS comes from the Sunnis who are facing religious discrimination of the Maliki government in Iraq. Therefore, with US pressure, Prime Minister of Iraq Maliki was replaced by Haider Al-Abadi as Iraqi PM in 2014. Weeks earlier Fuad Masum, a Kurd, became the new president of Iraq. But despite these changes, there was no lull in ISIS activities and now it started to move northwards to crush the Kurds.
But efforts intensified to counter ISIS when they uploaded youtube videos of beheading two US journalists and US missionary.
Iran – Shia dominated state – also felt threatened by ISIS and therefore joined Iraqi forces to defend holy places.
As of Now – 2019
In 2014, ISIS captured land in both Iraq and Syria. Different sects were not only fighting with each other but also ISIS forces. In 2017, with combined efforts, areas were retaken from Islamic State as ISIS started losing the control it once had. Though the war is still far from over, regional and international powers disagree on a settlement. Many Syrians have fled to neighbouring countries like Turkey, Jordon, Lebanon, Egypt and Iraq. Many refugees fled to start a new life in European countries. In Iraq and Syria, Islamic State remnants have retreated into the desert awaiting new opportunities.

3 comments
Got the understanding of ISIS …
nice!!
Very well explained. Thank you!
Comments are closed.